Do you want to change date and time format in WordPress website? By default, your posts will automatically display the inbuilt date and time set on your website. However, as a site owner, you may want to configure it and set it on your own format. It does not require any coding skills to do that. WordPress comes with an inbuilt option to configure the date and time format of your website.
Let’s check this out in detail:
The first thing you need to do is login to your WordPress dashboard.
Then, go to Settings > General.
After that, you need to scroll down to the Date Format. There, select the available date format and time format from their respective section.
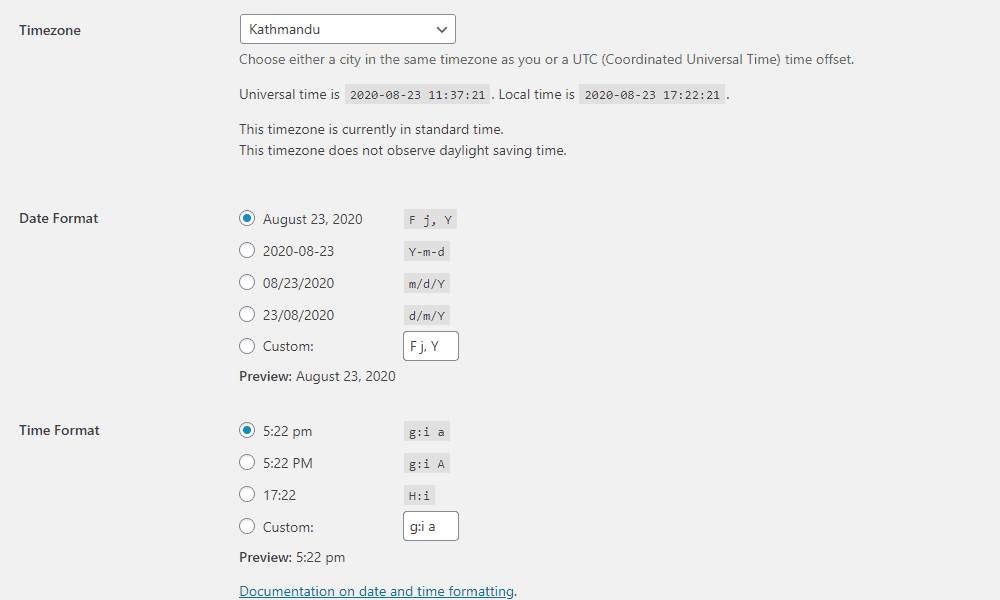
Then, choose the time zone as per the location you want to set.
If all the selection is fine, click on Save Changes below to save changes.
What are the Format Characters for Date and Time in WordPress?
Date and Time Format uses alphabetic character for representation. These are called formatting strings.
There are several predefined date constant that uses formatting parameter string. They are:
| Days | — | — |
| d | Day of the month, 2 digits with leading zeros | 01 to 31 |
| D | A textual representation of a day, three letters | Mon through Sun |
| j | Day of the month without leading zeros | 1 to 31 |
l (lowercase ‘L’) | A full textual representation of the day of the week | Sunday through Saturday |
| N | ISO-8601 numeric representation of the day of the week (added in PHP 5.1.0) | 1 (for Monday) through 7 (for Sunday) |
| S | English ordinal suffix for the day of the month, 2 characters | st, nd, rd or th. Works well with j |
| w | Numeric representation of the day of the week | 0 (for Sunday) through 6 (for Saturday) |
| z | The day of the year (starting from 0) | 0 through 365 |
| Week | — | — |
| W | ISO-8601 week number of year, weeks starting on Monday | Example: 42 (the 42nd week in the year) |
| Month | — | — |
| F | A full textual representation of a month, such as January or March | January through December |
| m | Numeric representation of a month, with leading zeros | 01 through 12 |
| M | A short textual representation of a month, three letters | Jan through Dec |
| n | Numeric representation of a month, without leading zeros | 1 through 12 |
| t | Number of days in the given month | 28 through 31 |
| Year | — | — |
| L | Whether it’s a leap year | 1 if it is a leap year, 0 otherwise. |
| o | ISO-8601 week-numbering year. This has the same value as Y, except that if the ISO week number (W) belongs to the previous or next year, that year is used instead. (added in PHP 5.1.0) | Examples: 1999 or 2003 |
| Y | A full numeric representation of a year, 4 digits | Examples: 1999 or 2003 |
| y | A two digit representation of a year | Examples: 99 or 03 |
| Time | — | — |
| a | Lowercase Ante meridiem and Post meridiem | am or pm |
| A | Uppercase Ante meridiem and Post meridiem | AM or PM |
| B | Swatch Internet time | 000 through 999 |
| g | 12-hour format of an hour without leading zeros | 1 through 12 |
| G | 24-hour format of an hour without leading zeros | 0 through 23 |
| h | 12-hour format of an hour with leading zeros | 01 through 12 |
| H | 24-hour format of an hour with leading zeros | 00 through 23 |
| i | Minutes with leading zeros | 00 to 59 |
| s | Seconds with leading zeros | 00 through 59 |
| u | Microseconds (added in PHP 5.2.2). Note that date() will always generate 000000 since it takes an integer parameter, whereas DateTime::format() does support microseconds if DateTime was created with microseconds. | Example: 654321 |
| v | Milliseconds (added in PHP 7.0.0). Same note applies as for u. | Example: 654 |
| Timezone | — | — |
| e | Timezone identifier (added in PHP 5.1.0) | Examples: UTC, GMT, Atlantic/Azores |
I (capital i) | Whether or not the date is in daylight saving time | 1 if Daylight Saving Time, 0 otherwise. |
| O | Difference to Greenwich time (GMT) without colon between hours and minutes | Example: +0200 |
| P | Difference to Greenwich time (GMT) with colon between hours and minutes (added in PHP 5.1.3) | Example: +02:00 |
| T | Timezone abbreviation | Examples: EST, MDT … |
| Z | Timezone offset in seconds. The offset for timezones west of UTC is always negative, and for those east of UTC is always positive. | -43200 through 50400 |
| Full Date/Time | — | — |
| c | ISO 8601 date (added in PHP 5) | 2004-02-12T15:19:21+00:00 |
| r | » RFC 2822 formatted date | Example: Thu, 21 Dec 2000 16:01:07 +0200 |
| U | Seconds since the Unix Epoch (January 1 1970 00:00:00 GMT) | See also time() |
From above-mentioned strings, here are some of the commonly used date and time formatting string are:
M d, Y – will output – Nov 06, 2014
d M, Y – will output – 06 Nov, 2014
F jS, Y – will output – November 6th, 2014
l, F jS, Y – will output – Thursday, November 6th, 2014
H:i:s – will output – 21:26:12
You can try the different formats on the custom box to change the format of both date and time on your WordPress website.
After you enter the format, WordPress will preview the date or time you have entered.
Once you have saved your settings, it will use this format throughout your website unless your theme has any type of pre-defined date and time format.

